Managing collections of data is an essential task for any application, but it can quickly become complex when you need to keep track of the relationships between different collections. For instance, if you have two collections of data, such as movies and reviews, you may need to retrieve all the reviews associated with a particular movie. However, writing complex code to retrieve this data and merge it together manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
That's where one of Appwrite’s newest features comes in. Database relationships help you manage the links between your collections of data more easily. With this feature, you can create links between different collections by simply adding a new attribute to them. You can choose from four types of relationships: one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many.
Relationship Types
One to One
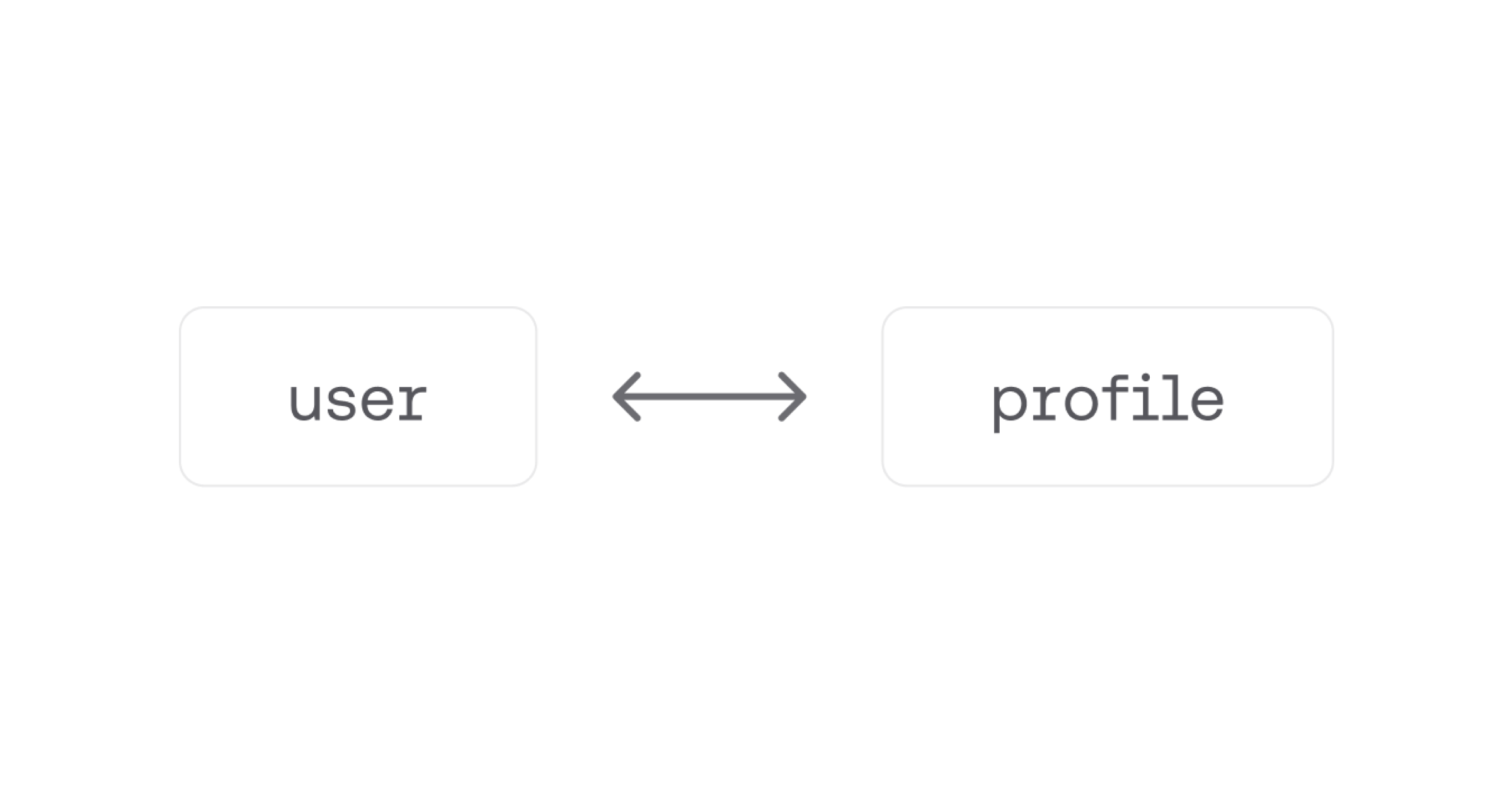
A one-to-one relationship means that each record in one collection is associated with only one record in another collection. For example, if you have a collection of users and a collection of profiles, each user can have only one profile, and each profile can belong to only one user.
One to Many
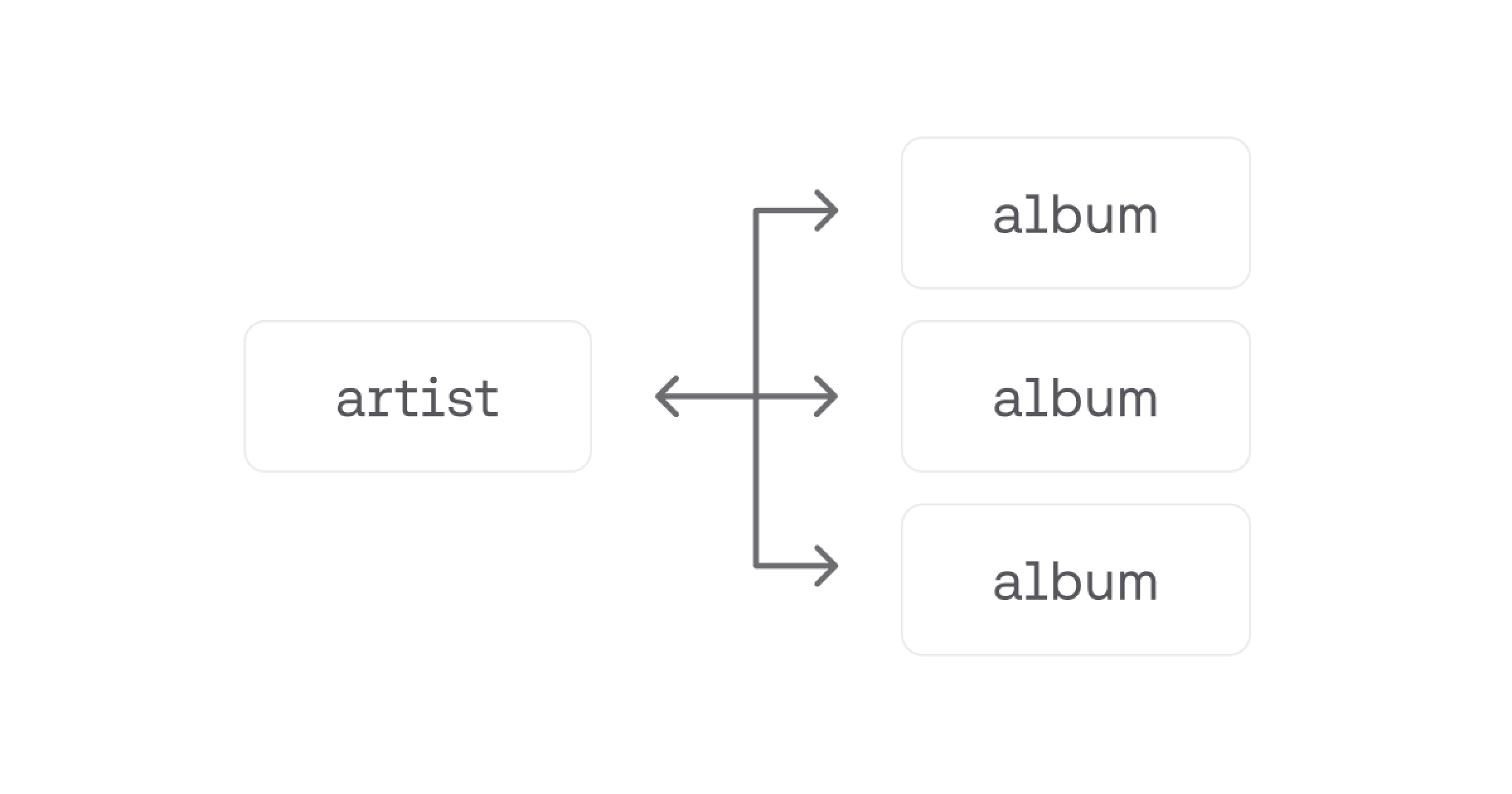
A one-to-many relationship is when each record in one collection can be associated with multiple records in another collection. For instance, if you have a collection of artists and a collection of albums, each artist can have many albums released, but each album can only be released by one artist.
Many To One
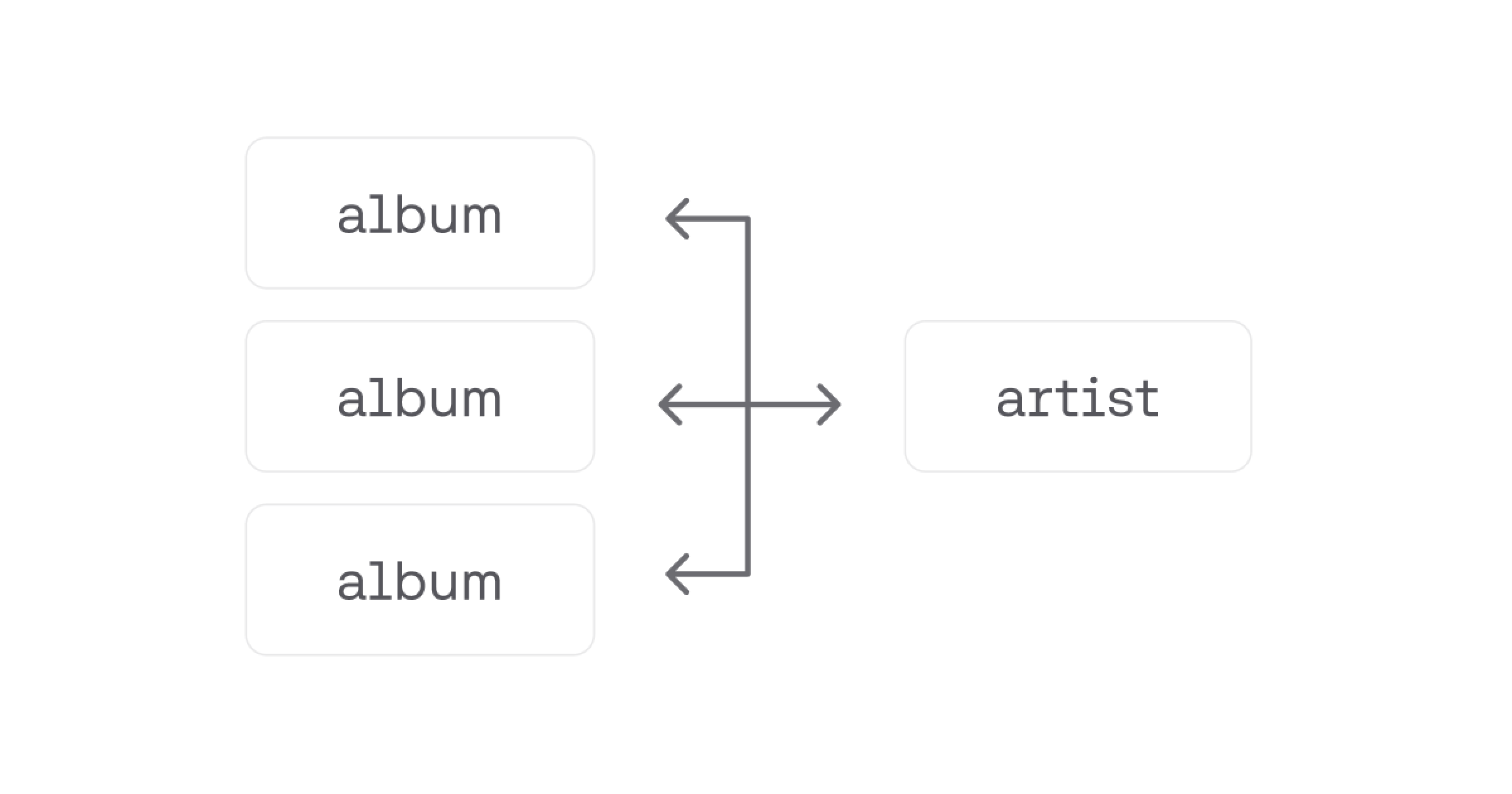
In contrast, many-to-one relationships are when multiple records in one collection can be associated with a single record in another collection. Inversely to the previous example, if you have a collection of albums and a collection of artists, many albums can be released by a single artist. While this may seem the same as a one-to-many relationship, it differs once you take the direction into account. A many-to-one relationship that is one-way can be used to represent a relationship that is only seen on the many side.
Many to Many
Finally, many-to-many relationships describe a scenario where multiple records in one collection can be associated with multiple records in another collection. For example, if you have a collection of books and a collection of authors, each book can have multiple authors, and each author can write multiple books.
By understanding the differences between these relationship types, you can choose the best one that suits your application's needs and create a more efficient database management system.
Relationship Directions
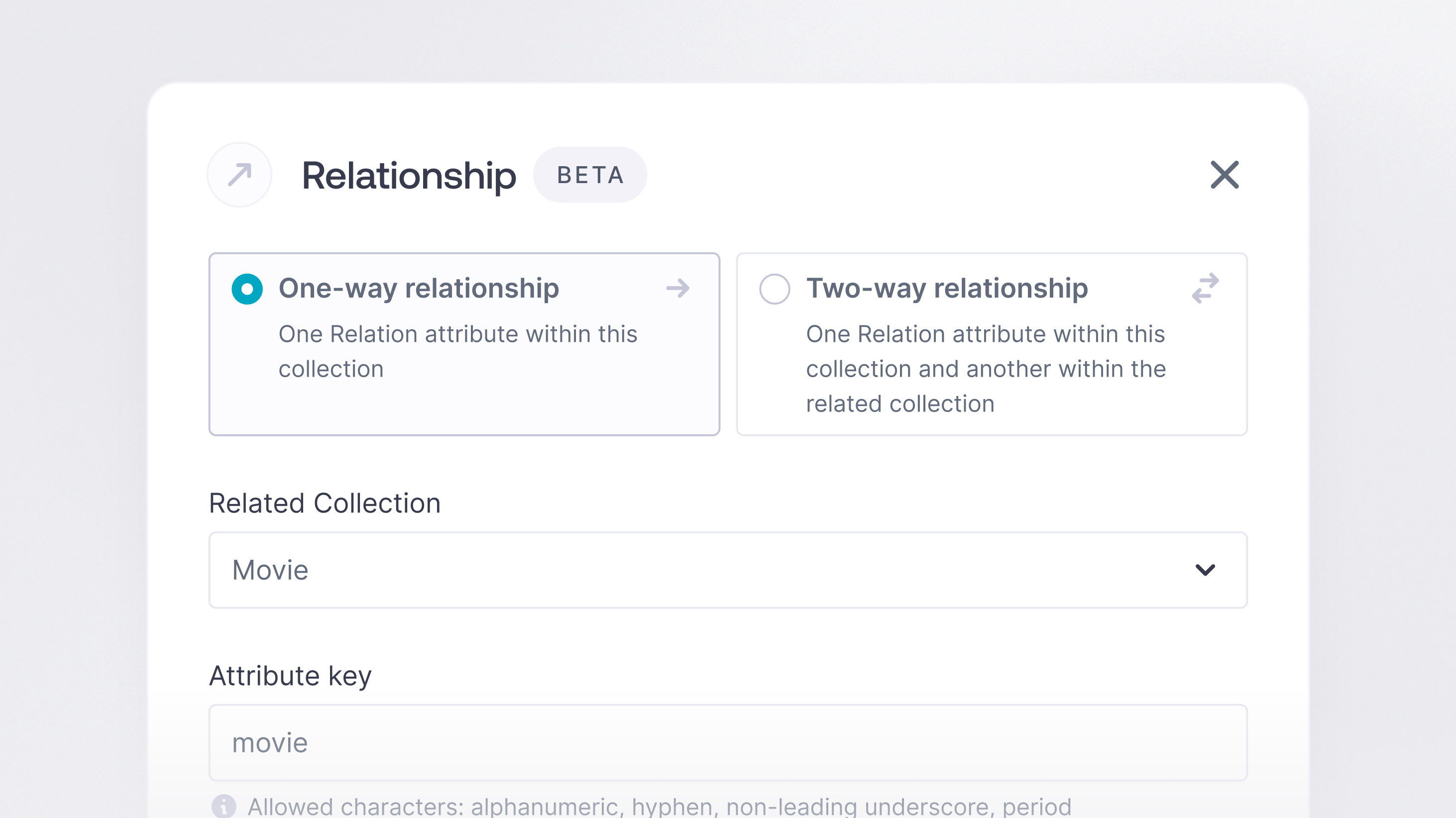
Appwrite relationships offer a high degree of flexibility and customization, allowing developers to create various scenarios with the available options. In addition to choosing from the four relationship types, developers can also decide whether the relationship should be one-way or two-way.
One Way
One-way relationships are a type of relationship where only the collection where the relationship attribute was created will see the relationship. For example, suppose a developer creates a one-way relationship between a movies collection and a reviews collection. In that case, the movies collection will have an attribute containing the related reviews, but the reviews collection will not have an attribute containing the related movie. This type of relationship is useful in scenarios where the parent collection holds all the necessary information, and the child collection only needs to access the parent's data.
The movie response:
{
"$id": "642b9afc785532a807d8",
"$databaseId": "marvel",
"$collectionId": "movies",
"$createdAt": "2023-04-04T03:35:24.493+00:00",
"$updatedAt": "2023-04-04T03:35:24.493+00:00",
"$permissions": [
],
"title": "Spiderman",
"reviews": [
{
"$id": "642b9d627d866e646602",
"$databaseId": "marvel",
"$collectionId" :"reviews",
"$createdAt": "2023-04-04T03:45:38.514+00:00",
"$updatedAt": "2023-04-04T03:45:38.514+00:00",
"$permissions": [
],
"content": "Great movie"
}
]
}
The review response, notably with no review attribute:
{
"$id": "642b9d627d866e646602",
"$databaseId": "marvel",
"$collectionId": "reviews"
"$createdAt": "2023-04-04T03:45:38.514+00:00",
"$updatedAt": "2023-04-04T03:45:38.514+00:00",
"$permissions": [],
"content": "Great movie"
}
Two Way
On the other hand, a two-way relationship is a type of relationship where both collections will see the relationship. In the same example, if a two-way relationship is created between the movies and reviews collections, both collections will have attributes containing the related data. This type of relationship is beneficial in scenarios where both the parent and child collections need to access each other's data.
The movie response:
{
"$id": "642b9afc785532a807d8",
"$databaseId": "marvel",
"$collectionId": "movies",
"$createdAt": "2023-04-04T03:35:24.493+00:00",
"$updatedAt": "2023-04-04T03:35:24.493+00:00",
"$permissions": [],
"title": "Spiderman",
"reviews": [
{
"$id": "642b9d627d866e646602",
"$databaseId": "marvel",
"$collectionId": "reviews",
"$createdAt": "2023-04-04T03:45:38.514+00:00",
"$updatedAt": "2023-04-04T03:45:38.514+00:00",
"$permissions": [],
"content": "Great movie"
}
]
}
The review response, now with the movie attribute:
{
"$id": "642b9d627d866e646602",
"$databaseId": "marvel",
"$collectionId": "reviews",
"$createdAt": "2023-04-04T03:45:38.514+00:00",
"$updatedAt": "2023-04-04T03:45:38.514+00:00",
"$permissions": [],
"content": "Great movie",
"movie": {
"$id": "642b9afc785532a807d8",
"$databaseId": "marvel",
"$collectionId": "movies",
"$createdAt": "2023-04-04T03:35:24.493+00:00",
"$updatedAt": "2023-04-04T03:35:24.493+00:00",
"$permissions": [],
"title": "Spiderman"
}
}
One-way and two-way relationships offer different advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific requirements of the application. In some cases, one-way relationships can provide better performance by reducing the amount of data that needs to be stored and accessed. However, two-way relationships can provide more flexibility by allowing both collections to access each other's data.
On Delete Behavior
Managing related data can still be challenging, especially when deleting data. To address this, Appwrite relationships offer three deletion strategies: restrict, cascade, and set null.
Restrict
If you select the restrict option, you won't be able to delete a parent document if it has any related child documents. This option is helpful if you want to ensure that data integrity is maintained and that you don't accidentally delete data that is still relevant.
Cascade
If you choose cascade, deleting a parent document will also delete all related child documents. This option can be helpful if you want to remove all data associated with a particular parent record, such as when you want to delete a user and all their associated data.
Set Null
Finally, the set null option means that deleting a parent document will remove the relationship to the parent document for all of its related children. This can be useful if you want to retain the child's records but simply remove the relationship.
Each of these options has its own use cases, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific application requirements. By providing these different options, Appwrite allows you to manage related data in a flexible and intuitive way, making it easier for you to build complex applications without worrying about data management.
Other Benefits
In addition to simplifying your collection management, database relationships also provide several other benefits. First, they can help to ensure data consistency and integrity by enforcing referential constraints between related collections. This means that you can prevent orphaned documents or other data inconsistencies that might arise if you were to manage the relationships between collections manually. Additionally, using relationships can also improve the performance of your requests and reduce the amount of code you need to write, since you can retrieve related data in a single request rather than having to fetch it separately.
Overall, database relationships are a powerful tool that simplifies your collection management and saves you time and effort. By easily linking your collections and retrieving related data, you can focus on developing your application's core features. Check out the docs for more information. We encourage you to give it a try today and see how it can benefit your development process.