Learn how to setup your first Python project powered by Appwrite.
Head to the Appwrite Console.
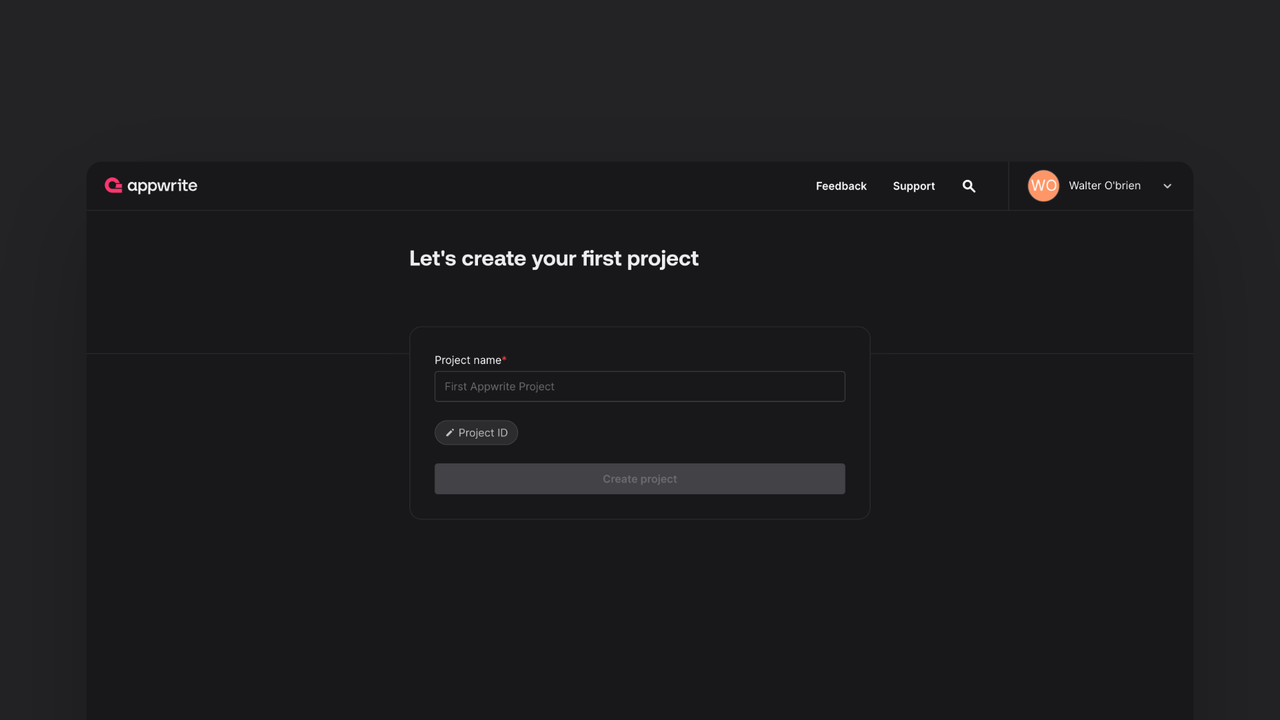
If this is your first time using Appwrite, create an account and create your first project.
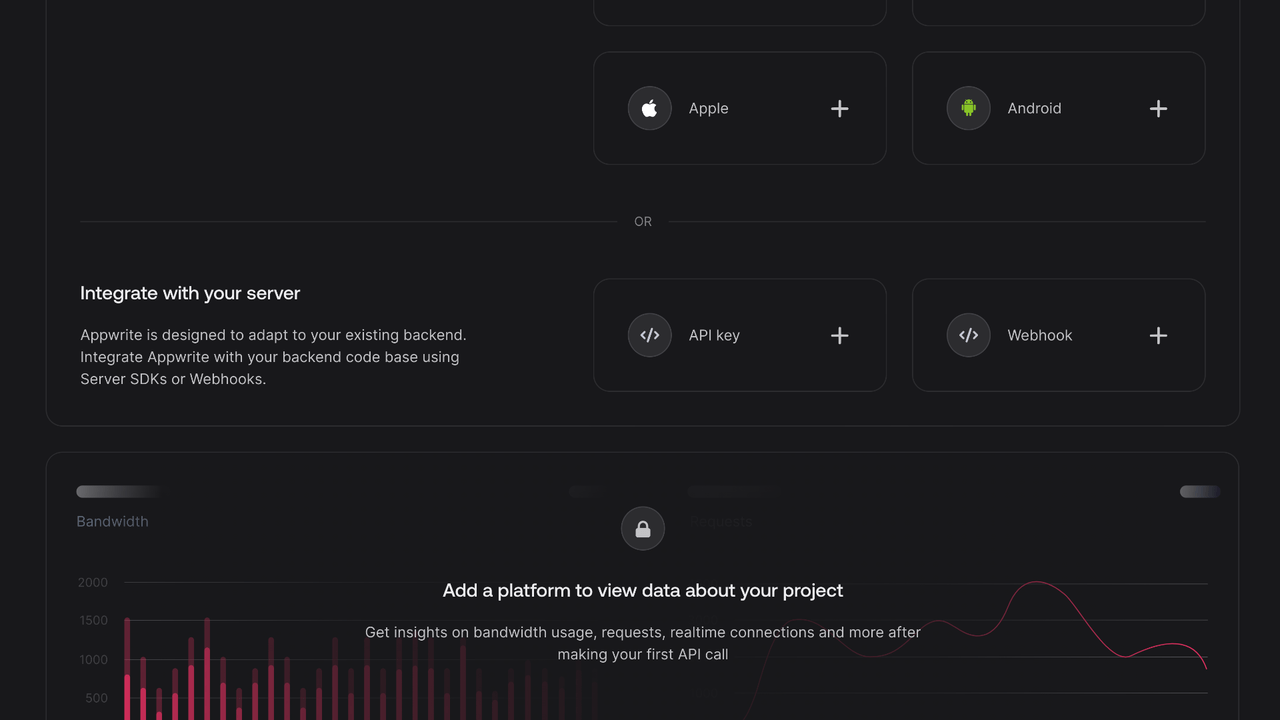
Then, under Integrate with your server, add an API Key with the following scopes.
| Category | Required scopes | Purpose |
Database | databases.write | Allows API key to create, update, and delete databases. |
tables.write | Allows API key to create, update, and delete tables. | |
columns.write | Allows API key to create, update, and delete columns. | |
rows.read | Allows API key to read rows. | |
rows.write | Allows API key to create, update, and delete rows. |
Other scopes are optional.
Create a directory for the project.
mkdir my_app
cd my_app
After that, create a virtual environment in this directory and activate it.
# Create a venv
python -m venv .venv
# Active the venv in Unix shell
source .venv/bin/activate
# Or in Powershell
.venv/Scripts/Activate.ps1
Finally, create a file my_app.py.
Install the Python Appwrite SDK.
pip install appwrite==13.6.1
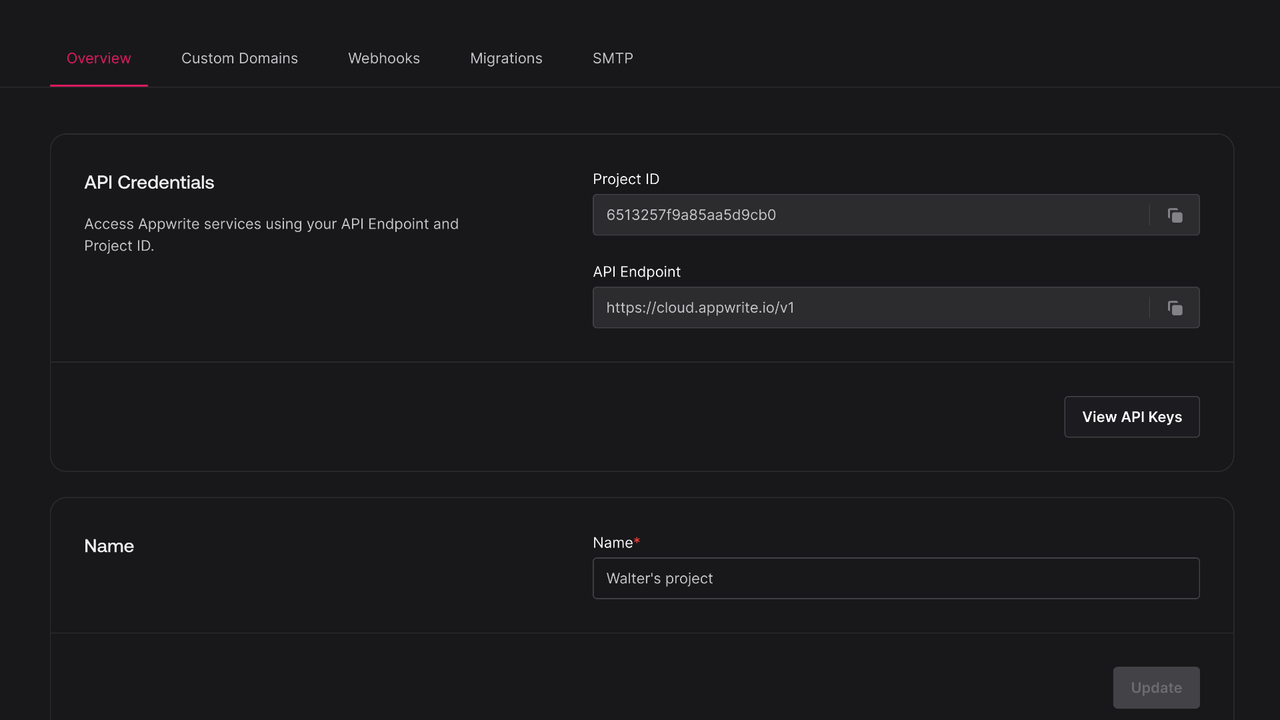
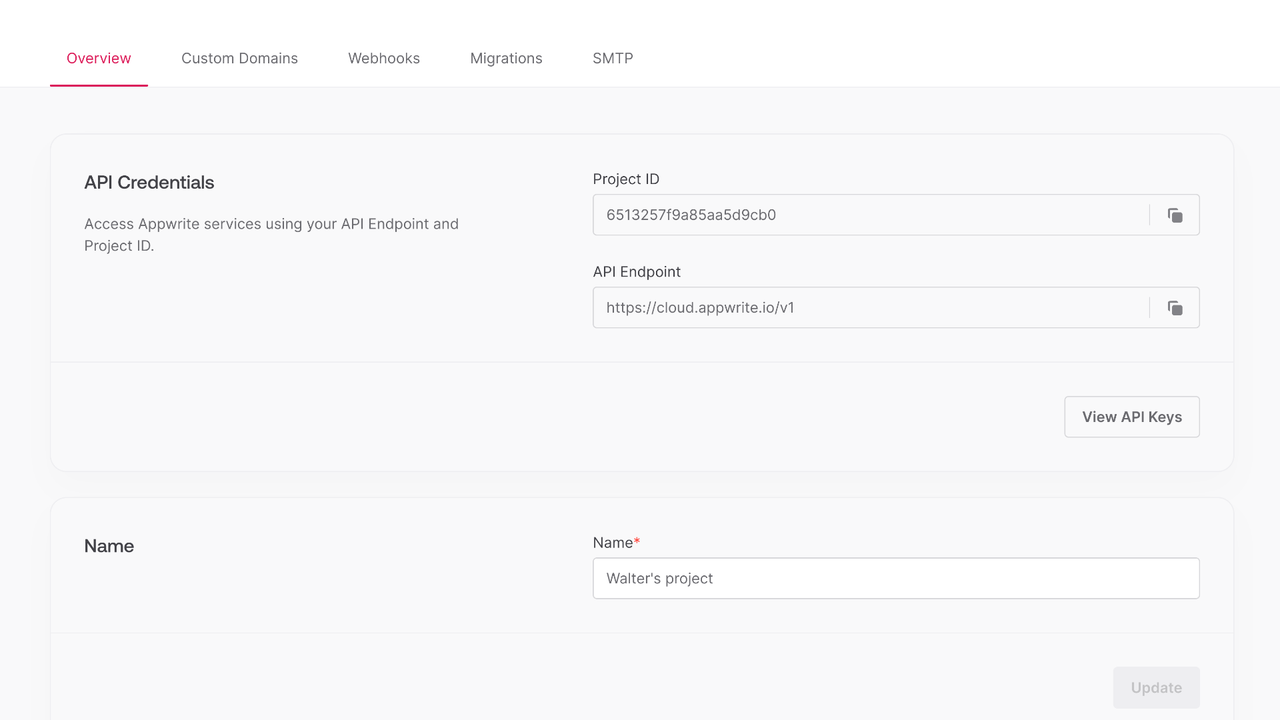
Find your project ID in the Settings page. Also, click on the View API Keys button to find the API key that was created earlier.


Open my_app.py and initialize the Appwrite Client. Replace <PROJECT_ID> with your project ID and <YOUR_API_KEY> with your API key.
from appwrite.client import Client
from appwrite.services.tables_db import TablesDB
from appwrite.id import ID
client = Client()
client.set_endpoint('https://<REGION>.cloud.appwrite.io/v1')
client.set_project('<PROJECT_ID>')
client.set_key('<YOUR_API_KEY>')
Once the Appwrite Client is initialized, create a function to configure a todo table.
tablesDB = TablesDB(client)
todoDatabase = None
todoTable = None
def prepare_database():
global todoDatabase
global todoTable
todoDatabase = tablesDB.create(
database_id=ID.unique(),
name='TodosDB'
)
todoTable = tablesDB.create_table(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=ID.unique(),
name='Todos'
)
tablesDB.create_varchar_column(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id'],
key='title',
size=255,
required=True
)
tablesDB.create_text_column(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id'],
key='description',
required=False,
default='This is a test description.'
)
tablesDB.create_boolean_column(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id'],
key='isComplete',
required=True
)
Create a function to add some mock data into your new table.
def seed_database():
testTodo1 = {
'title': "Buy apples",
'description': "At least 2KGs",
'isComplete': True
}
testTodo2 = {
'title': "Wash the apples",
'isComplete': True
}
testTodo3 = {
'title': "Cut the apples",
'description': "Don\'t forget to pack them in a box",
'isComplete': False
}
tablesDB.create_row(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id'],
row_id=ID.unique(),
data=testTodo1
)
tablesDB.create_row(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id'],
row_id=ID.unique(),
data=testTodo2
)
tablesDB.create_row(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id'],
row_id=ID.unique(),
data=testTodo3
)
Create a function to retrieve the mock todo data, then execute the functions in _main_.
from appwrite.query import Query
def get_todos():
# Retrieve rows (default limit is 25)
todos = tablesDB.list_rows(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id']
)
print("Todos:")
for todo in todos['rows']:
print(f"Title: {todo['title']}\nDescription: {todo['description']}\nIs Todo Complete: {todo['isComplete']}\n\n")
def get_completed_todos():
# Use queries to filter completed todos with pagination
todos = tablesDB.list_rows(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id'],
queries=[
Query.equal("isComplete", True),
Query.order_desc("$createdAt"),
Query.limit(5)
]
)
print("Completed todos (limited to 5):")
for todo in todos['rows']:
print(f"Title: {todo['title']}\nDescription: {todo['description']}\nIs Todo Complete: {todo['isComplete']}\n\n")
def get_incomplete_todos():
# Query for incomplete todos
todos = tablesDB.list_rows(
database_id=todoDatabase['$id'],
table_id=todoTable['$id'],
queries=[
Query.equal("isComplete", False),
Query.order_asc("title")
]
)
print("Incomplete todos (ordered by title):")
for todo in todos['rows']:
print(f"Title: {todo['title']}\nDescription: {todo['description']}\nIs Todo Complete: {todo['isComplete']}\n\n")
if __name__ == "__main__":
prepare_database()
seed_database()
get_todos()
get_completed_todos()
get_incomplete_todos()
Run your project with python my_app.py and view the response in your console.